Kiwa PVEL
Key Takeaways
Breakage Rates
Glass//backsheet and hail-hardened module designs have lower breakage rates.
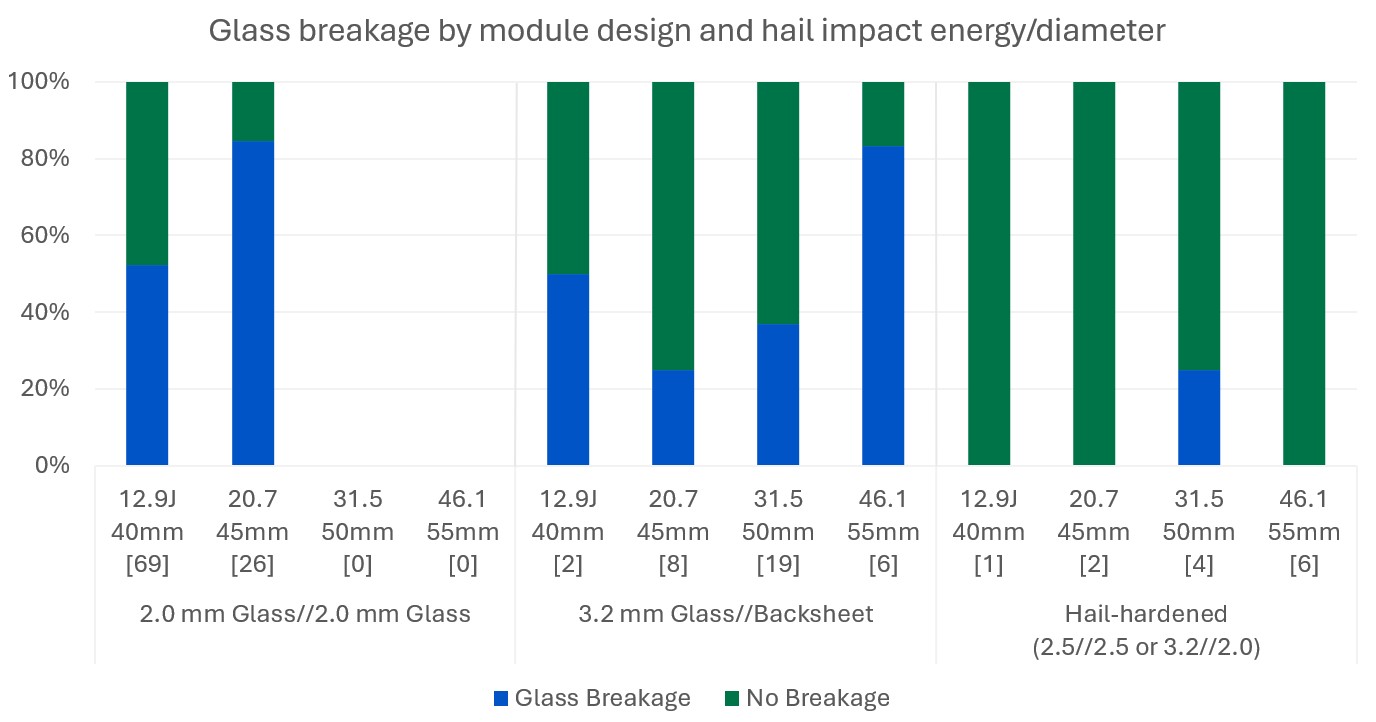
The past year of testing continued to prove that 3.2 mm glass//backsheet modules and hail-hardened designs are significantly less susceptible to glass breakage than 2.0 mm glass//2.0 mm glass modules (see the Test Result Spotlight below). The HSS Top Performer category highlights modules resistant to glass breakage for 40 mm hail and greater.

Hail-hardened Modules
Initial glass//glass modules with thicker glass show improved hail resistance.
The first BOMs of hail-hardened modules made with either 2.5 mm glass//2.5 mm glass or 3.2 mm glass//2.0 mm glass have achieved lower glass breakage rates than both 3.2 mm glass//backsheet and 2.0 mm glass//2.0 mm glass. This is an encouraging example of the value of climate-specific module designs. See the Test Result Spotlight below for more.

Minimal Power Loss
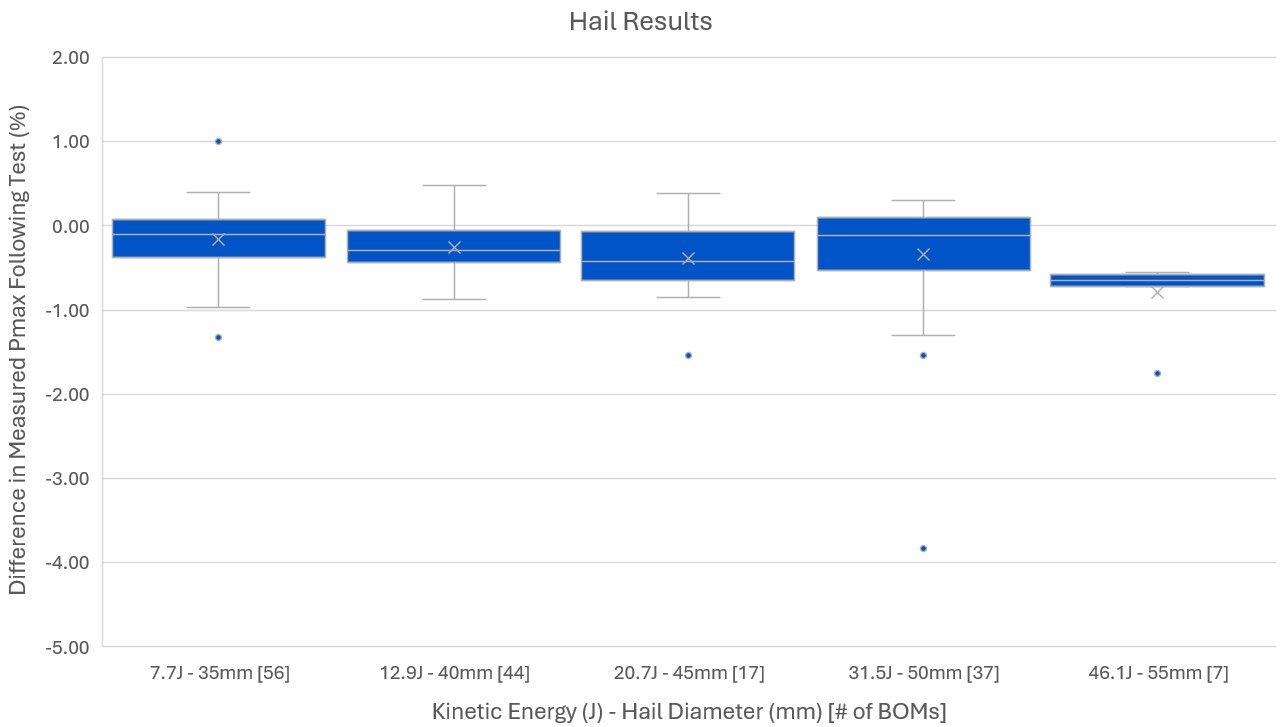
No post-hail impact power degradation > 2% in the 2025 Scorecard dataset.
Glass//glass modules continue to show minimal power loss as cells are protected from cracking within the neutral plane. Branching cell cracks have been observed on glass//backsheet modules following hail testing, but ultimately these modules suffer relatively little hail-induced power loss due to the use of half-cut, multi-bus bar (MBB) cells. See the Power Degradation graph below for more.
Failures Rise
Broken modules from both hail sizes and hail retests were most prevalent.
HSS failures are recorded if modules break when tested at both hail sizes, which happened most with 2.0 mm glass//2.0 mm glass modules breaking at both 35 and 40 mm. A failure is also recorded when a manufacturer requests a hail retest due to glass breakage. 15% of BOMs experienced at least one of these two cases. See the Failures page for more.

Hail Test Results Spotlight
The glass breakage rates from Kiwa PVEL’s hail testing of almost 300 PQP modules from the 2025 Scorecard dataset is shown below. The results are separated by 2.0 mm glass//2.0 mm glass, 3.2 mm glass//backsheet and “hail-hardened” modules. The hail-hardened category represents a mix between 2.5 mm glass//2.5 mm glass and 3.2 mm glass//2.0 mm glass, which are marketed as being able to withstand larger hail than traditional module designs. Kiwa PVEL’s results show the increased hail durability of 3.2 mm glass//backsheet modules compared to 2.0 mm glass//2.0 mm glass. The hail durability advantages of hail-hardened modules are also clearly shown, although the sample sizes for these modules are limited thus far.